10.1
While learning organic chem, you’ll have come across many homologous series. In all the homologous series you’ve come across, the repeating units are CH2 groups.
- Alkanes and Alkenes
- Carboxylic acids
- Ketones
- Aldehydes
- Alcohols
- Nitriles
Explanation of the trends in boiling points of members of a homologous series.
As the chain length increases in a homologous series, the boiling point increases. This is because as the chain length increases, so do the London Dispersion forces.
STRUCTURAL FORMULAS AND STRUCTURAL ISOMERISM
Full Structural Formula
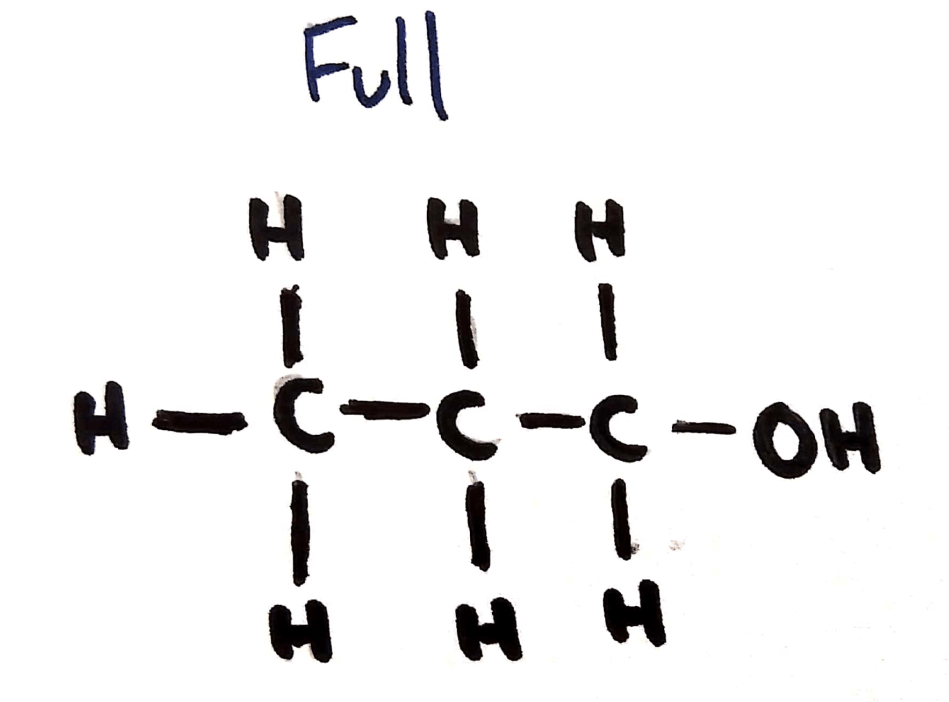
Shown:
- Hydrogens
- Carbons
- All other atoms
- All bonds
Condensed Structural Formula
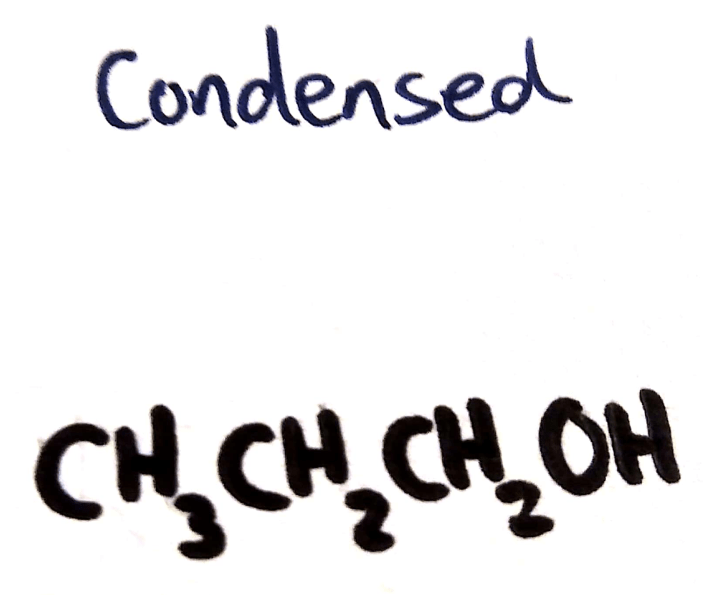
Shown:
- Hydrogens
- Carbons
- All other atoms
Not shown
- Bonds
Skeletal Formula
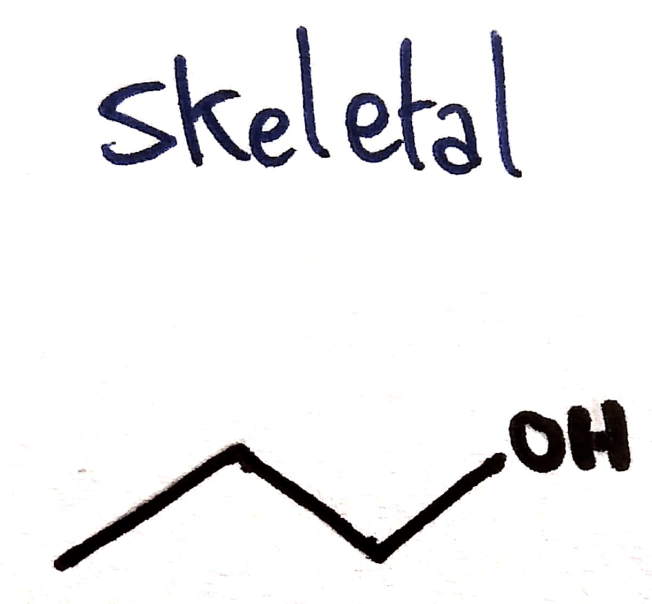
Shown:
- Carbons (as corners’)
- All other atoms
- Show all bonds
Not shown:
- Hydrogens
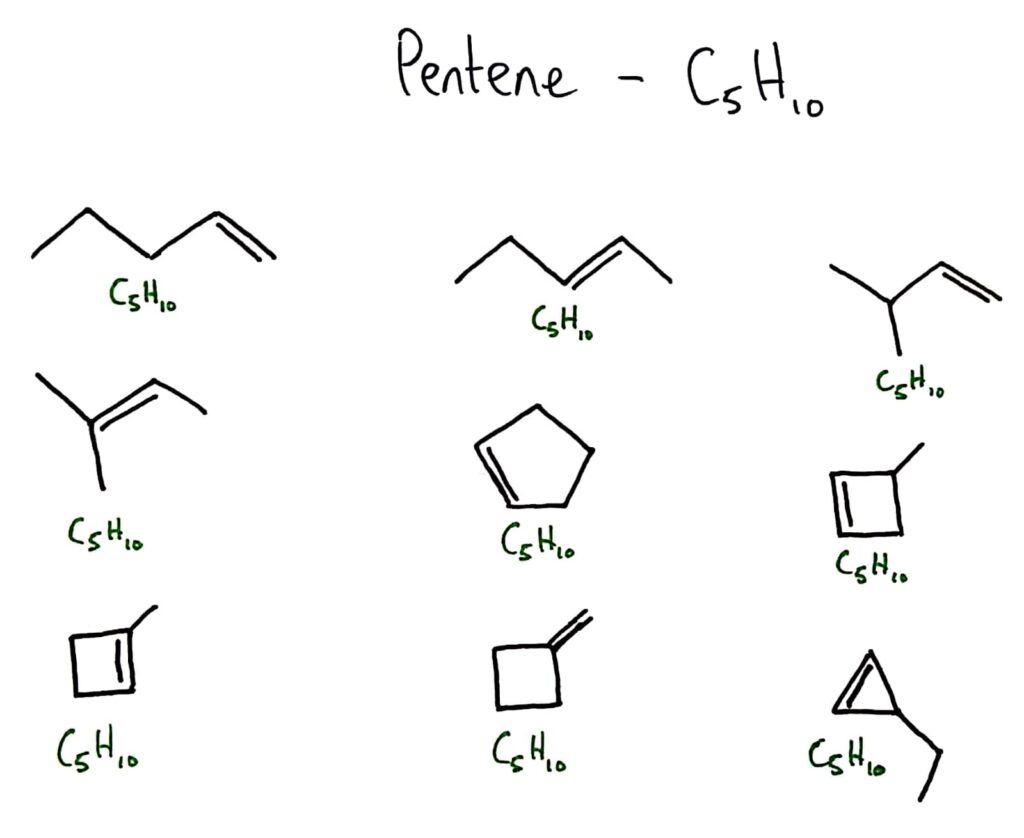
Structural isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms.
There are quite a few different arrangements for different numbers of atoms, there is no one set way for them to bond. This leads to structural isomers like below.
NOTE: Not all isomer below are isomers of pentene but all are isomers of C5H10
Molecular
The total number of each atom present in the molecule.
Empirical
The smallest ratio of the numbers of atoms present in the molecule.
FUNCTIONAL GROUPS AND BASIC ORGANIC CHEM
The functional group of the molecule is the part of the molecule that reacts with other organic molecules as you’ll see in topic 10.2 and 20 when you study reaction mechanisms.
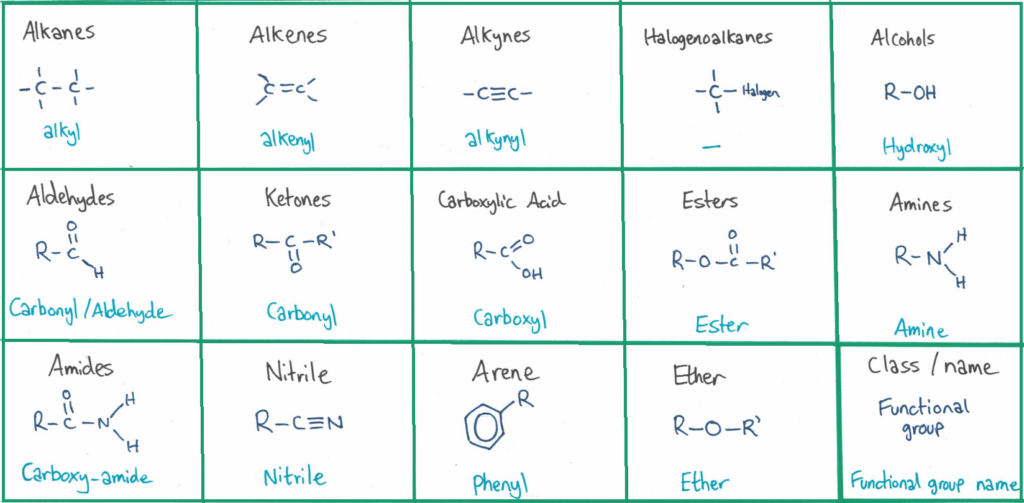
You need to memorise and be able to identify these organic functional groups. I’ve created a couple of quizlet sets for this (more later in the post).
Hopefully you’ve learnt this before and this is just a recap. A fully saturated molecule contains ONLY single bonds. If it contains any double or triple bonds, it’s unsaturated.
Aromatic compounds are cyclic compounds that have resonance (topic 4+14). Benzene is unsaturated because of it’s 3 resonant double bonds.
How we know benzene is resonant:
- Enthalpy of combustion is not consistent with 3 double bonds
- Enthalpy of hydration is also not consistent with 3 double bonds
- Bond lengths of all 6 bonds in the ring are equal, the bonds are therefore all equal strength
- Benzene does not undergo addition reactions (e.g with Br) like other alkenes
Construction of 3-D models (real or virtual) of organic molecules.
Application of IUPAC rules in the nomenclature of straight-chain and branched-chain isomers.
Organic molecule naming quizlet:
Identification of primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms in halogenoalkanes and alcohols and primary, secondary and tertiary nitrogen atoms in amines.
Whether an alcohol, amide or halogenoalkane is primary secondary or tertiary depends on the number of carbon atoms are bonded to the carbon atom that’s bonded to the functional group. It might take you a while to get your head around this but there’s a quiz down below that should be able to help.